But how does NFC compare to traditional microcellulose (MCC)? Understanding these differences is key to choosing the right material for your formulation needs.
Microcellulose, particularly microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), has been widely used in the pharmaceutical industry since the 1960s as a powder-based excipient. It functions as a filler to bulk up tablets and capsules, an absorbent to reduce moisture, a binder for wet granulation and direct compression, an anti-adherent to prevent aggregation, and a stabilizer that extends drug release. Additionally, MCC is commonly used as an anti-caking agent, emulsifier, foam stabilizer, starch extender, and fat substitute. Its granule size typically ranges from tens to hundreds of microns. In contrast, nanofibrillar cellulose (NFC) is an advanced hydrogel that is relatively new to pharmaceutical applications.
Unlike MCC, NFC is a highly biocompatible material with superior water retention and processability, making it ideal for injectable and implantable medical applications. It was first introduced to the market in FibDex®—a CE-marked, ISO 13485-certified advanced wound dressing—and is now undergoing first-in-human trials as a bulking agent for medical implants. Offering unique structural and functional properties not found in other cellulose-based materials, NFC represents a new frontier in pharmaceutical and biomedical applications.
Better Biocompatibility, Injectability, Emulgation, and Superior Water Retention with ISO 13485 Natural Material
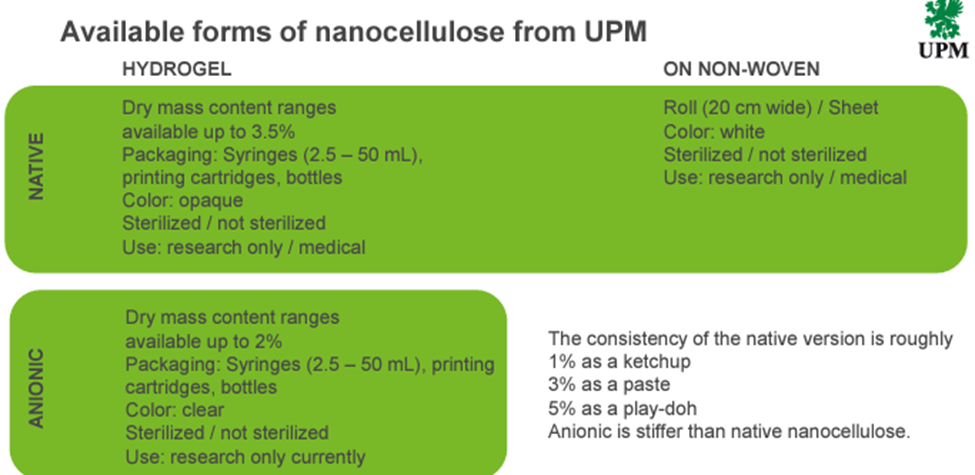
Nanofibrillar cellulose provides the highest water retention capacity among all cellulosic materials and is a true hydrogel. Unlike microcellulose, which consists of large micron-sized particles, NFC is composed of fibers only a few tens of nanometers in diameter and tens of microns in length, making its structure similar to collagen fibers. This nanoscale size gives NFC exceptional functional advantages, including:
- Better biocompatibility – Interacts naturally with cells and tissues, ensuring safe medical use
- Injectability & Shear-Thinning – Suitable for medical implants, soft tissue repair, and drug delivery
- Superior Water Retention – Provides moisture stability for sensitive pharmaceutical formulations
- Emulsification Capability – Naturally prevents sedimentation, making it ideal for liquid formulations
Unlike MCC, which is typically available as a powder, NFC is a stable hydrogel that does not sediment and naturally enhances emulsion stability, making it highly suitable for pharmaceutical, biomedical, and life science applications.